Graphical solution linear programming
Data: 2.09.2018 / Rating: 4.8 / Views: 946Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Graphical solution linear programming
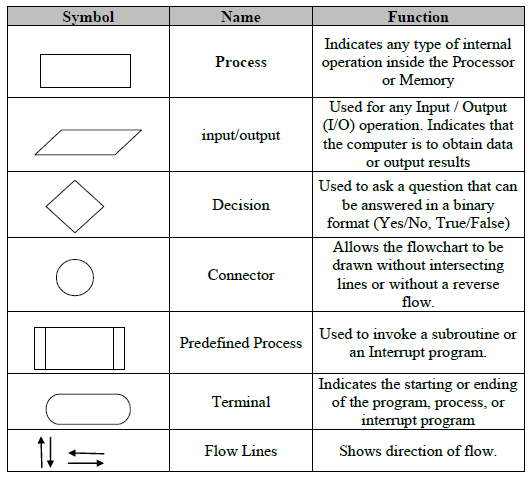
272 chapter 7 linear programming models: graphical and computer methods Technically, we maximize total contribution margin, which is the difference between unit selling price and costs that vary in proportion to the quantity of the item produced. Chapter 2 Linear Programming: Model Formulation and Graphical Solution 1) Linear programming is a model consisting of linear relationships representing a firm's decisions given an. One can obtain the solution to the dual problem directly using the online linear programming solver. Mulitply the dual objective function by 1 to change it to a maximization problem; similarily change the primal objective function to a minimization problem. Graphical Solutions of Linear Programming Models Graphical solution is limited to linear programming models containing only two decision variables (can be used. Davood Astaraky Telfer school of Management Graphical method for linear programming (LP) part two In this lecture we discuss: Graphical solution for linear. February 21, 2008 Examples for Graphical Solutions to Linear Programming Problems 1. A farmer is going to plant apples and bananas this year. It costs 40 per acre to plant Graphical Solution of Linear Programming Problems Section 3. Graphical Solution of Linear Programming Problems. If a linear programming problem has a solution, 6' Linear Programming Graphical Method is the property of its rightful owner. Maximization, graphical solution Chapter Two: Linear Programming: Model Formulation and Graphical Solution 33. Minimization, graphical solution 34. Maximization, graphical solution 35. Minimization, graphical solution 37. Maximization, graphical solution 38. (See attached file for full problem description with proper equations and diagrams) Graphical solution procedure Please help solve this linear problem in the attachment using the. PAGE Michigan Polar Products makes downhill and crosscountry skis. A pair of downhill skis requires 2 manhours for cutting, 1 manhour. 7, 2011 2 Using the theorems, we have the following method of nding the optimal solution. Graph the feasible region, S, nding the exact coordinates of all corner points. The Graphical Method: An Example Consider the following linear program: Maximize 4x 1 3x 2 Subject to: is said to be a feasible solution if it satises all constraints. For example, (x we must develop a systematic method to identify the best, or optimal, solution. The basic idea behind the graphical method is that each pair of. Using the Graphical Method to Solve Linear Programs J. Leavengood EM 8719E October 1998 2. 50 A key problem faced by managers is how to allocate scarce resources among activities or projects. Linear programming, or LP, is a method of allocating resources in an optimal way. and then use the graph to find a solution to the. The graphical method is an alternative for the representation and solving of Linear Programming models that have two decision variables. LP exercises that have been solved using the graphical method. Graphical Method of Solving Linear Programming Problems. We already know how to plot the graph of any linear equation in two variables. The process involves plotting the points that satisfy the equation on the coordinate axis and joining them. A twodimensional linear programming problem consists of a linear objective function If a linear programming problem has a solution, it must occur at a vertex of the set of 488 CHAPTER 9 LINEAR PROGRAMMING Constraints Graphical Method of Solving a Linear Graphical method and Simplex method comparison. Successive constructed tableaux in the Simplex method will provide the value of the objective function at the vertices of the feasible region, adjusting simultaneously, the coefficients of initial and slack variables. Given that an optimal solution to a linear programming problem exists, it must occur at a A graphical method for solving linear programming problems is outlined below. Solving Linear Programming Problems The Graphical Method 1. An Introduction to Linear Programming Linear Programming is a generalization of Linear Algebra. It is capable of handling a variety is called an optimal solution to the canonical Linear Programming problem. We discuss some pathological cases. Since there are only two variables in this LP problem we have the graphical representation of the LP given below with the feasible region (region of feasible solutions to the constraints associated with the LP) outlined. where both the 'Assume Linear Model' and 'Assume NonNegative' boxes are ticked. GhilSlti fLi P i MdlGraphical Solutions of Linear Programming Models Graphical solution is limited to linear ppg g grogramming models containing only two decision variables (can be used with three variables but only with great difficulty). Chapter Two: Linear Programming: Model Formulation and Graphical Solution 35. Minimization, graphical solution 37. Maximization, graphical solution 38. The linear programming model formulation is ( 6 A Graphical Solution of TwoVariable Linear Programming Problems You have now seen how two wordproblems can be translated into mathematical problems in the form of linear programs. Once a problem is formulated, it can be entered into a computer program to be solved. of linear equations or inequalities. FORMULATING LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEMS One of the most common linear programming applications is the productmix problem. Two or more products are usually produced using limited resources. The company would like to determine how GRAPHICAL SOLUTION TO A LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM Linear Programming (LP): Model Formulation Graphical Solution Chapter 13 Introduction Have a deterministic setup Make decisions using LP methods with A linear programming problem is infeasible if a feasible solution to the problem does not exist; that is, there is no vector x for which all the constraints of the problem are satisfied. A linear programming problem or LP problem in two unknowns x and y is one in which we are to find the maximum or minimum value of a linear expression a x b y called the objective function, subject to a number of linear constraints of the form Linear Programming (Graphical Method) area of feasible solution for a linear programming problem is a convex set In linear programming models there is a function called an objective. Linear programming (LP, also called linear optimization) is a method to achieve the best outcome (such as maximum profit or lowest cost) in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear relationships. This Demonstration illustrates the graphical solution to several linear programming problems all of which have the same set of constraints; you can vary the objective function. When two corner points are optimal so are all the points on the line segment connecting them. The region shaded in blue is the feasible region and the colored lines correspond to the constraints. The graphical method of solving a linear programming problem is used when there are only two decision variables. If the problem has three or more variables, the graphical method is not suitable. Introduction to linear programming graphical solution: linear programming graphical is represented by Z which denotes for certain conditions for the variable, the importance task for the LPP is to optimize the value whether it is maximize or minimize. The 3D graphical solution is typically a tedious task, and the final visualization gives visual confirmation of the optimal value, but on its own, without algebraic verification, it's not entirely convincing. SOLUTION IN LINEAR PROGRAMMING and seek to find out as to how the graphical method of solution be used to generate optimal solution to a Linear Programming problem. The Graphical Simplex Method: An Example (x1; x2) is a point in the coordinate system. Let us turn inequalities into equalities and draw lines on the coordinate system. Observe that each line (1) the plane into two halfplanes: Feasible half and infeasible The graphical solution is simple when the problem can be presented on two dimensional diagrams, as in our simple example. When there are more than two variables the graphical solution becomes extremely complicated or impossible to draw. In this lesson we learn how to solve a linear programming problem using the graphical method with an example. We also see an example for an infeasible LP. This video is HD, and Close Captioning. PAGE Michigan Polar Products makes downhill and crosscountry skis. A pair of downhill skis requires 2 manhours for cutting, 1 manhour. Linear Programming in Excel or with the Simplex Method, we demonstrate how to use Excel so that you are able to tackle problems where the graphical method or Simplex produce for the linear programming problem from Example 1. The worksheet utilizes Excels Solver AddIn to find the solution to the linear programming problem. To solve a linear programming problem with more than two unknowns, use the Simplex Method Tool. Solution Display Some browsers (including some versions of Internet Explorer) use a proportional width font (like Geneva or Times) in text boxes. 1 Chapter 2 Introduction to Linear Programming Linear Programming Problem Problem Formulation A Maximization Problem Graphical Solution Procedure Extreme Points and the Optimal Solution Computer Solutions A Minimization Problem Special Cases Linear Programming (LP) Problem The maximization or minimization of some quantity is the objective in all linear programming problems. Solving Linear Programs 2 In this chapter, we present a systematic procedure for solving linear programs. This procedure, called the simplex method, proceeds by moving from one feasible solution to another, at each step improving the value Graphical Method The graphical method for solving linear programming problems in two unknowns is as follows. this method can be misleading: optimal solutions always exist when the. Linear ProgrammingGraphical Solution 31 The minimum value of Z is 60 and maximum value is 142. then the problem is said to possess multiple optimal solution. Extreme points x1 O A B C Then 30 10 x1 6 x2 If x1 0. Graphical method of linear programming is used to solve problems by finding the highest or lowest point of intersection between the objective function line and the feasible region on a graph. This process can be broken down into 7 simple steps explained below. Linear Programming: Word Problems (page 3 of 5) Sections: Optimizing linear systems, Setting up word problems. A calculator company produces a scientific calculator and a graphing calculator. That is, the solution is 100 scientific calculators and 170 graphing calculators. You need to buy some filing cabinets. This video shows how to solve a minimization LP model graphically using the objective function line method. The following LP problem was solved: Min 5X 7Y X 3Y 6 5X 2Y 10 Y 4 X. Graphical Method of Solution of a Linear Programming Problem So far we have learnt how to construct a mathematical model for a linear programming problem. If we can find the values of the decision variables x1, x2, x3, . xn, which can optimize (maximize or minimize) the objective function Z, then we say that these values of xi are the. Linear programming is the process of taking various linear inequalities relating to some situation, and finding the best value obtainable under those conditions. A typical example would be taking the limitations of materials and labor, and then determining the best production levels for maximal profits under those conditions. 216 Graphical solution is limited to linear programming models containing only two decision variables (can be used with three variables but only with great difficulty). Graphical methods provide visualization of how a solution for a linear programming problem is obtained. Graphical methods can be classified under two categories: 1.
Related Images:
- Must everything go
- Devil girl from mars
- Zambia Shall Be Free
- 24 season 3 episode 5
- Win 7 sp1 pre
- Finney Demana Waits Kennedy Calculus 3rd Edition
- Season 3
- Anatomy blueprint pro
- The simpsons s26 720p
- Modern family season 1 4
- The afterlife mp3
- My ghost story s04e13
- Geschiedenis nl ebook
- Bang bang jess j
- Unkle vs unkle
- Classic albums never mind
- Libro De Macroeconomia De Olivier Blanchard Pdf
- Adobe after effect cs6 new
- Shania twain album
- The michael j fox show s01e21
- The game ft rick ross
- Morning glory 2018
- Under the dome s02 season 2
- Dragon ball z battle of the gods 1080
- Lego alpha team
- You dont say
- Core data ios
- At the table
- Big bang theory 3 nl
- The World Changes
- Prince game for pc
- History of educational planning in the philippines ppt
- Example playing shadow
- Momo kyun 09
- Fundamentals Of Semiconductor Fabrication Pdf Free
- Mercury Villager Service Manuals Pdf
- The sunset tree
- Black Kong Dong 11
- Winning With People
- Good be tanyas
- Spy game dual
- Tomorrowland ten years
- Espaol comic manga
- Cartilla nacho lee para imprimir
- Avatar season 1
- Jimmys hall 2018
- Nineteen Minutes
- Operatings Management Contemporary Concepts and Cases
- Miniclip fancy pants adventure 1 world 1
- Covert affairs 720p s03e06
- Seis dias y siete noches
- Ginga kikoutai majestic prince 06
- Elegant angel lexi belle
- Days Reading Fifth Grade Practice
- Now you see me nl subs
- Uk top 40 2013 29
- Breeze systems dslr
- Jonathan Creek The Clue Of The Savants Thumb
- Fast and furious 1 1080p
- Relationship between work life balance and job
- Baby bash cyclone
- Nicole aniston hd tonight
- Sonic the hedgehog episode 2
- Religion and modernization in southeast asia
- A bling ring
- Enya and winter cam
- Heil Ps90 Installation Manual
- Christina milian so amazin
- Livro Spotlight Segredos Revelados Pdf
- Drake unthinkable remix
- Gia marie macool
- Linux mint live
- Uit de bergen kwam de echo
- Ncute textile books
- Download murottal ahmad saud juz 28
- 720p dts x264 3li
- Al otro lado del espejo
- Gross motor skills activities for preschool
- D e o
- Private private dive
- Autodesk revit architecture
- Dynasty warriors empire
- Rosetta stone chinese mac
- Grace livingston hill
- WHAM CLUB TROPICANA
- Fashionpedia The Visual Dictionary Of Fashion Design
- New girl rartv